Among the many processes that fulfil the stringent requirements of modern manufacturing, injection molding is one of the greatest innovations in efficiency and precision.
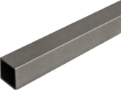
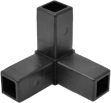
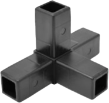
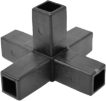
From producing intricate components for automotive engines to crafting everyday consumer products, injection molding is a versatile and indispensable method. We’ve discussed how our aluminum tubes are formed, what aluminium is, and what steel is, but how are EZ Tube advanced composite connectors made, and how do they work? Let’s dive into the intricacies of this transformative manufacturing process.
Understanding Injection Molding
Injection molding is a manufacturing technique used to produce parts by injecting molten material into a mold cavity under high pressure. This process allows for the creation of complex shapes with exceptional accuracy and repeatability. Common materials used in injection molding include thermoplastics, thermosetting polymers, and elastomers, each selected based on the desired properties of the final product.
The Injection Molding Process
The manufacturing process consists of several distinct stages, each crucial to achieving precise and consistent results:
- Mold Creation: The process begins with the design and fabrication of a mold, which serves as the negative of the desired part. Molds are typically made from steel or aluminum and are precision-machined to exact specifications.
- Material Preparation: Granular or pelletized material is fed into a hopper, where it undergoes melting and homogenization in a heated barrel. The material is then injected into the mold cavity through a nozzle and runner system.
- Injection: Once the material reaches the desired temperature and viscosity, a reciprocating screw or plunger forces it into the mold cavity under high pressure. This pressure ensures that the material completely fills the mold and achieves uniform distribution.
- Cooling: After injection, the molten material undergoes rapid cooling, solidifying into the shape of the mold cavity. Cooling time is carefully controlled to optimize part quality and minimize cycle times.
- Ejection: Once the part has sufficiently cooled and solidified, the mold opens, and the finished part is ejected using ejector pins or mechanisms. The mold then closes, ready for the next cycle.
Key Advantages
Injection molding offers numerous advantages over alternative manufacturing methods, including:
- High Precision: Injection molding allows for the production of intricate and highly detailed parts with tight tolerances. This high precision is a key reason why EZTube leverages this manufacturing process across its advanced composite pipe fitting line.
- Cost Efficiency: Once molds are created, this can be highly cost-effective for large-volume production runs.
- Versatility: Injection molding can accommodate a wide range of materials and part geometries, making it suitable for diverse applications.
- Scalability: From small-scale prototyping to mass production, the scalability of this manufacturing can easily scale to meet varying production demands.
Industries
Injection molding finds application across a myriad of industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, medical devices, consumer goods, and more. From miniature components to large structural parts, this manufacturing process enables the creation of products that shape our daily lives.

EZTube connector for extruded aluminum tube
Injection molding is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering unparalleled precision, efficiency, and versatility. By harnessing the power of high-pressure injection, manufacturers can transform raw materials into complex, high-quality parts with remarkable speed and consistency. As technology continues to advance, this advanced manufacturing process remains at the forefront of innovation, driving progress and shaping the future of manufacturing. Shop for EZ Tube injection molded fittings today and explore how EZ Tube can work with you to create custom manufacturing solutions for your next product line.